NTFS vs exFAT: Which Is Better for USB and External Drives
When you format a new USB drive or external hard disk, Windows asks you to choose a file system like NTFS, exFAT, or FAT32. Many people pick one without knowing what it does. But your choice affects how fast the drive works, what devices can read it, and how large your files can be.
NTFS and exFAT are the two main file systems for Windows users. Both have unique advantages, and the right one depends on how and where you plan to use the drive.
What Is a File System

A file system is the basic structure your computer uses to organize and manage data on a drive. Every storage device — whether it’s a hard drive, SSD, or USB — relies on a file system to decide where and how your files are saved. Without it, your computer wouldn’t know where a file begins or ends.
Think of it like a digital filing cabinet. When you create or move a file, the file system records its name, size, and location so your computer can find it later. This structure ensures that even thousands of files stay organized and easy to access.
A file system also controls how data is stored and retrieved. It handles file names, folders, permissions, and even who can access specific files on a shared computer. This management system helps your device read and write data efficiently.
Main functions of a file system include:
- Storing and organizing file data.
- Managing file names, folders, and user access rights.
- Tracking available storage space and file size limits.
Different file systems serve different purposes. For example, NTFS focuses on performance and security, while exFAT focuses on compatibility and portability. That’s why choosing the right file system for your drive matters more than most people realize.
What Is NTFS
NTFS (New Technology File System) is Microsoft’s default file system for Windows drives. It was introduced in the early 1990s and is used in almost every internal hard drive or SSD that runs Windows today.
Main features of NTFS:
- Practically unlimited file size support.
- Advanced permissions and security options.
- Journaling system that protects data from corruption.
- Built-in compression and encryption features.
NTFS is stable and secure, making it perfect for internal drives and Windows system storage. However, macOS can only read NTFS by default, not write to it, which limits cross-platform use.
What Is exFAT
exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table) is also developed by Microsoft but designed for external storage like USB drives, SD cards, and portable SSDs. It’s a modern replacement for the older FAT32 format.
Main features of exFAT:
- Supports huge files up to 16 exabytes.
- Works on Windows, macOS, and many Linux systems.
- Lightweight and faster for portable drives.
- No journaling system (faster but less safe if power fails).
exFAT is ideal for people who share files between different operating systems or need a format that works everywhere without limits.
NTFS vs exFAT: Main Differences
Here’s a side-by-side comparison of NTFS and exFAT.
| Feature | NTFS | exFAT |
|---|---|---|
| Developer | Microsoft | Microsoft |
| File Size Limit | 16 TB+ | 16 EB |
| OS Support | Windows (full), macOS (read-only) | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| Security | Advanced permissions, encryption | None |
| Best For | Internal drives, Windows PCs | External drives, cross-platform use |
| Speed | Reliable and steady | Faster for flash storage |
NTFS focuses on data protection and stability, while exFAT focuses on speed and flexibility.
Compatibility Across Platforms
Each file system behaves differently depending on which operating system or device you use. Choosing the wrong format can cause problems when transferring files between computers or devices.
NTFS is fully supported by Windows, which means you can read and write files without any issues. It’s the standard choice for most Windows PCs. However, on macOS, NTFS drives are read-only by default — you can open files but can’t edit or save changes unless you install third-party software. On Linux, NTFS is partially supported, though newer versions often need extra drivers to work smoothly.
exFAT, on the other hand, is far more flexible. It works seamlessly on Windows, macOS, and most modern Linux systems. It’s also supported by smart TVs, digital cameras, and gaming consoles, which makes it ideal for portable drives and SD cards.
If you use both Windows and Mac computers or move files between multiple devices, exFAT is the better choice. It gives you smooth cross-platform compatibility without needing extra tools or drivers.
Pros and Cons of Each Format
NTFS Pros:
- Secure and reliable for system drives.
- Handles large files with no problem.
- Has built-in data protection and recovery tools.
NTFS Cons:
- Limited support outside of Windows.
- Slightly slower on small portable drives.
exFAT Pros:
- Compatible with many devices.
- Perfect for external drives and SD cards.
- Fast and lightweight.
exFAT Cons:
- No journaling or file recovery.
- More prone to corruption if disconnected suddenly.
Your choice depends on whether you need compatibility or security more.
When to Use NTFS
Choose NTFS if you mainly use Windows and store your files on a drive that stays connected to your computer. It’s built for stability, performance, and advanced file management. NTFS works best for drives that handle system files or large amounts of business and personal data.
It’s ideal for Windows system drives, where the operating system needs full access to advanced features like file permissions and encryption. NTFS is also great for business data, where security and reliability are more important than compatibility.
If you’re storing sensitive or encrypted information, NTFS provides better protection and consistency than other formats. Overall, it’s the best option for drives that need long-term stability and don’t need to work across multiple operating systems.
When to Use exFAT
Choose exFAT if you regularly transfer files between Windows and macOS, or if you use portable drives like USB sticks, external hard drives, or SD cards. It’s designed for convenience and cross-platform use, making it perfect for people who move data between different systems.
exFAT works well for USB drives and portable SSDs, since it handles large files without the limits found in older formats like FAT32. It’s also ideal for external hard drives used on multiple computers, letting you read and write data anywhere without compatibility issues.
If you often work with large video files, photos, or backups, exFAT is a smart choice. It provides excellent flexibility and ease of use, especially for users who prioritize portability over advanced security features.
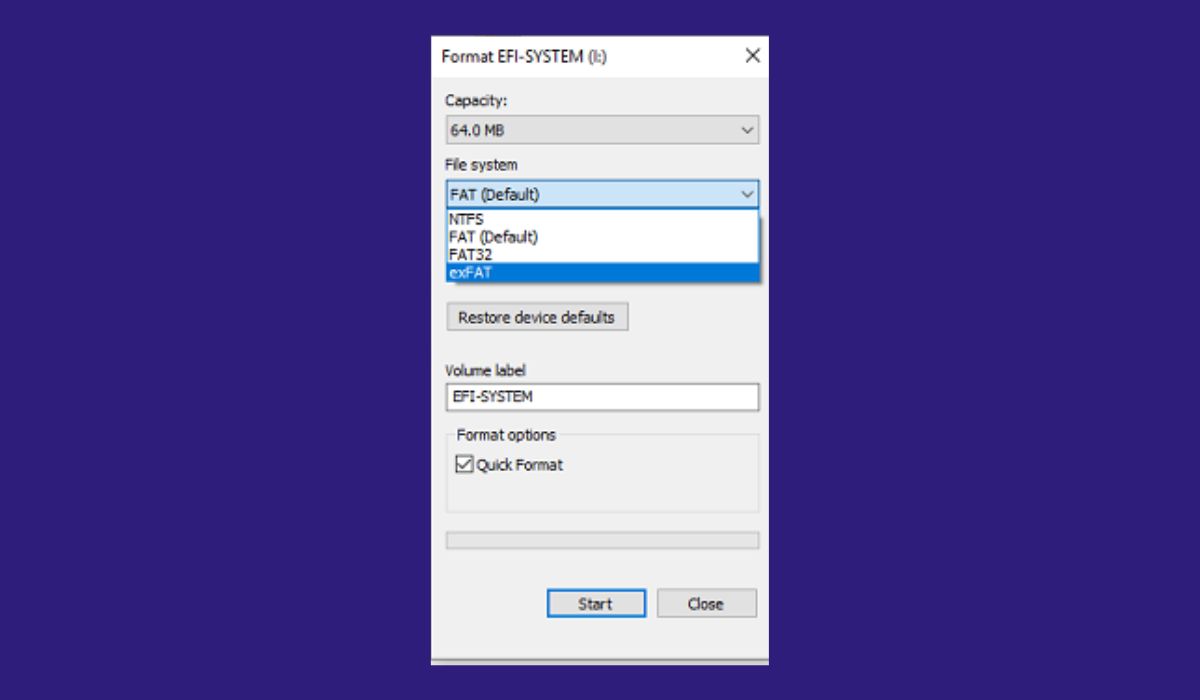
How to Format a Drive to NTFS or exFAT
Formatting a drive is easy on Windows, but it deletes all existing files, so back up your data first.
- Connect your drive to the computer.
- Open File Explorer → This PC.
- Right-click the drive and select Format.
- Choose NTFS or exFAT under File System.
- Click Start and wait for it to complete.
Once done, your drive is ready to use in the selected format.
Final Thoughts
Both NTFS and exFAT are excellent file systems — just for different purposes.
- Use NTFS for Windows drives that need security, stability, and advanced features.
- Use exFAT for external or cross-platform drives where flexibility and speed matter more.
If you want reliability on Windows, go with NTFS. If you share files between devices or systems, choose exFAT. Either way, picking the right format ensures your drive performs well and stays compatible wherever you use it.



